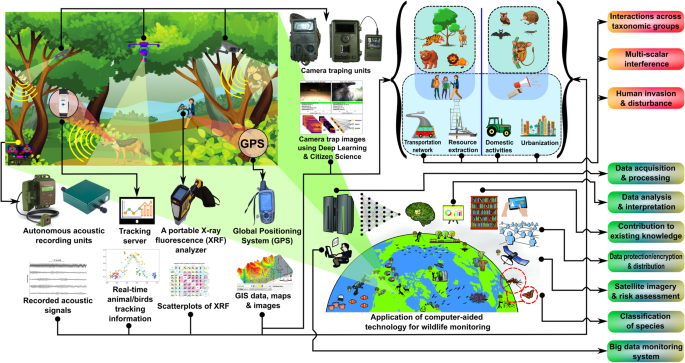
Monitoring gewas populations in remote areas has always been a challenge for conservationists due to the inaccessibility of these regions. However, recent advancements in technology have provided new, innovative strategies that are revolutionizing how we track and study these species.
One notable development is the use of satellite imagery combined with machine learning algorithms. Satellite technology allows for the observation of large, difficult-to-reach areas, while machine learning helps analyze patterns in the data, identifying potential gewas populations and tracking their movements. This method offers a non-intrusive way to monitor wildlife without disturbing their natural habitats.
Additionally, the deployment of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, has proven effective. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal sensors, drones can capture real-time data on gewas populations, even in dense forests or rugged terrain. This approach not only improves data accuracy but also enhances the efficiency of monitoring efforts.
Another breakthrough is the development of remote sensor networks. These sensors, placed in strategic locations, collect data on environmental conditions and animal activity. The data is transmitted via satellite, providing valuable insights into gewas behavior and habitat use.
These innovative strategies are transforming conservation efforts by providing more comprehensive, real-time information on gewas populations in remote areas. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more effective methods to ensure the protection and sustainability of these vital species.